Estimate noise model parameters#
Objects from thztools: noisefit, NoiseModel, NoiseModel.noise_amp, NoiseModel.noise_sim,scaleshift, timebase, wave.
[1]:
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import thztools as thz
Set the simulation parameters#
[2]:
n = 256 # Number of samples
m = 50 # Number of simulated waveforms
dt = 0.05 # Sampling time [ps]
sigma_alpha = 1e-4 # Additive noise amplitude [signal units]
sigma_beta = 1e-2 # Multiplicative noise amplitude [dimensionless]
sigma_tau = 1e-3 # Time base noise amplitude [ps]
Simulate an input waveform#
[3]:
t = thz.timebase(n, dt=dt)
mu = thz.wave(n, dt=dt)
Simulate measurements#
Define amplitude drift parameters a and delay drift parameters eta, each with length m - 1. Use the numpy.repeat function to generate an array of m copies of mu, then use scaleshift to rescale and shift all but the first of them by the elements a and eta, respectively. Use the transpose operation to orient the array so that the waveforms are arranged columnwise.
Next, create an instance of the NoiseModel class and use the noise_sim method to add simulated noise to each waveform.
[4]:
rng = np.random.default_rng(0)
a = 1.0 + 1e-2 * rng.standard_normal(m - 1)
eta = 1e-3 * rng.standard_normal(m - 1)
z = thz.scaleshift(
np.repeat(np.atleast_2d(mu), m, axis=0),
dt=dt,
a=np.insert(a, 0, 1.0),
eta=np.insert(eta, 0, 0.0)
).T
noise_model = thz.NoiseModel(
sigma_alpha=sigma_alpha,
sigma_beta=sigma_beta,
sigma_tau=sigma_tau,
dt=dt
)
x = z + noise_model.noise_sim(z, axis=0, seed=12345)
Fit a noise model to the simulated measurements#
[5]:
noise_res = thz.noisefit(
x,
sigma_alpha0=sigma_alpha,
sigma_beta0=sigma_beta,
sigma_tau0=sigma_tau,
dt=dt
)
print(f"{noise_res.noise_model.sigma_alpha=}")
print(f"{noise_res.noise_model.sigma_beta=}")
print(f"{noise_res.noise_model.sigma_tau=}")
noise_res.noise_model.sigma_alpha=0.00010072985446306559
noise_res.noise_model.sigma_beta=0.009849777070777796
noise_res.noise_model.sigma_tau=0.0008994024169028506
Compare the fitted noise model with an empirical noise estimate#
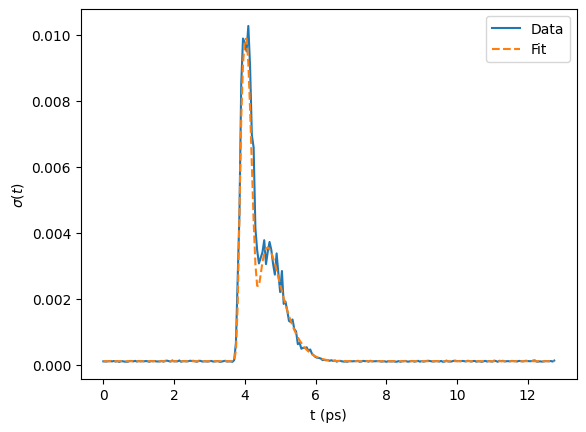
Use the fitted values noise_res.a and noise_res.eta with scaleshift to correct for drift in x. Determine the standard deviation at each time point of the resulting x_corrected array. Compare this to the fitted noise model using the noise_amp method of noise_res.noise_model with noise_res.mu.
[6]:
x_corrected = thz.scaleshift(
x, a=1 / noise_res.a, eta=-noise_res.eta, axis=0
)
plt.plot(t, np.std(x_corrected, axis=1), "-", label="Data")
plt.plot(t, noise_res.noise_model.noise_amp(noise_res.mu), "--", label="Fit")
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("t (ps)")
plt.ylabel(r"$\sigma(t)$")
plt.show()